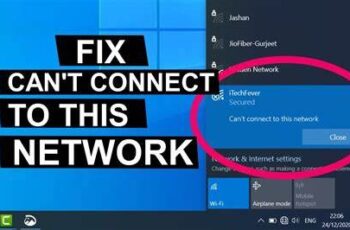
It can be frustrating when your Windows PC can’t connect to Wi-Fi, even though other devices on the same network work fine. This problem usually points to issues specific to your Windows machine, such as software glitches, driver problems, or configuration errors. This article explains in detail how to diagnose and fix the issue, based on recent research and personal troubleshooting experience.
Understanding the Problem
When other devices connect fine but your Windows PC can’t, it indicates that:
- The Wi-Fi network is working.
- The router is functioning.
- The issue is isolated to your Windows PC.
Step 1: Restart Your PC and Router
Start with the basics:
- Restart your Windows PC.
- Power cycle your router by unplugging it for 30 seconds and plugging it back in.
This often clears temporary glitches affecting connectivity.
Step 2: Forget and Reconnect to the Wi-Fi Network
Sometimes saved network credentials become corrupted.
- Click the Wi-Fi icon on the taskbar.
- Right-click your Wi-Fi network and select Forget.
- Reconnect by selecting the network and entering the password.
This resets your connection profile.
Step 3: Run the Windows Network Troubleshooter
Windows has a built-in troubleshooter that can fix common network issues:
- Open Settings > Network & Internet > Status.
- Click Network troubleshooter.
- Follow the prompts to detect and fix problems.
This automated tool often identifies simple fixes.
Step 4: Check Airplane Mode and Wi-Fi Adapter
Ensure airplane mode is off and Wi-Fi adapter is enabled:
- Click the action center icon (bottom right).
- Verify Airplane mode is off.
- Check that Wi-Fi is turned on.
- Open Device Manager (press Windows + X).
- Expand Network adapters.
- Right-click your Wi-Fi adapter and select Enable if disabled.
Step 5: Update Wi-Fi Drivers
Outdated or corrupted drivers can prevent Wi-Fi connections.
- Open Device Manager.
- Right-click your Wi-Fi adapter and select Update driver.
- Choose Search automatically for updated driver software.
- If Windows doesn’t find a new driver, visit your PC manufacturer’s website to download the latest.
I often found that updating drivers resolved connectivity issues.
Step 6: Reset Network Settings
Resetting network settings can fix misconfigurations:
- Open Settings > Network & Internet > Advanced network settings.
- Click Network reset.
- Click Reset now and confirm.
- Your PC will restart.
This removes and reinstalls network adapters and resets settings.
Step 7: Check IP Configuration
Incorrect IP settings can block internet access:
- Open Command Prompt as administrator.
- Run the following commands one by one:
- ipconfig /release
- ipconfig /renew
- ipconfig /flushdns
This refreshes your IP and clears DNS cache.
Step 8: Disable VPN or Security Software Temporarily
Sometimes VPNs or firewalls interfere with network access.
- Temporarily disable any VPN or security software.
- Try reconnecting to Wi-Fi.
- If this fixes the problem, adjust software settings or contact support.
Step 9: Change DNS Settings
Switching to a public DNS can help:
- Open Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi > Hardware properties.
- Scroll to IP settings and click Edit.
- Set to Manual and enable IPv4.
- Enter DNS addresses like Google’s DNS:
- Preferred: 8.8.8.8
- Alternate: 8.8.4.4
- Save and test connection.
Step 10: Disable Power Management for Wi-Fi Adapter
Windows may turn off the adapter to save power:
- Open Device Manager.
- Right-click your Wi-Fi adapter > Properties.
- Go to Power Management tab.
- Uncheck Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power.
- Click OK.
This prevents unexpected disconnections.
Step 11: Check Router Settings
Although other devices connect, router settings like MAC filtering may block your PC:
- Access your router’s admin panel (usually via 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1 in browser).
- Check if MAC filtering is enabled.
- If yes, add your PC’s MAC address or disable filtering.
Step 12: Create a New Network Profile
Sometimes the existing profile is corrupted.
- Open Command Prompt as admin.
- Run netsh wlan show profiles to list Wi-Fi profiles.
- Run netsh wlan delete profile name=”YourNetworkName” to delete the problematic profile.
- Reconnect to the network to create a fresh profile.
Step 13: Check for Windows Updates
Microsoft often releases fixes for network problems:
- Open Settings > Windows Update.
- Click Check for updates.
- Install any available updates and restart.
Conclusion
When Windows can’t connect to Wi-Fi but other devices can, the issue usually lies in your PC’s network settings, drivers, or configuration. Following these steps systematically—starting from basic restarts to advanced driver updates and network resets—will help you resolve the problem effectively.