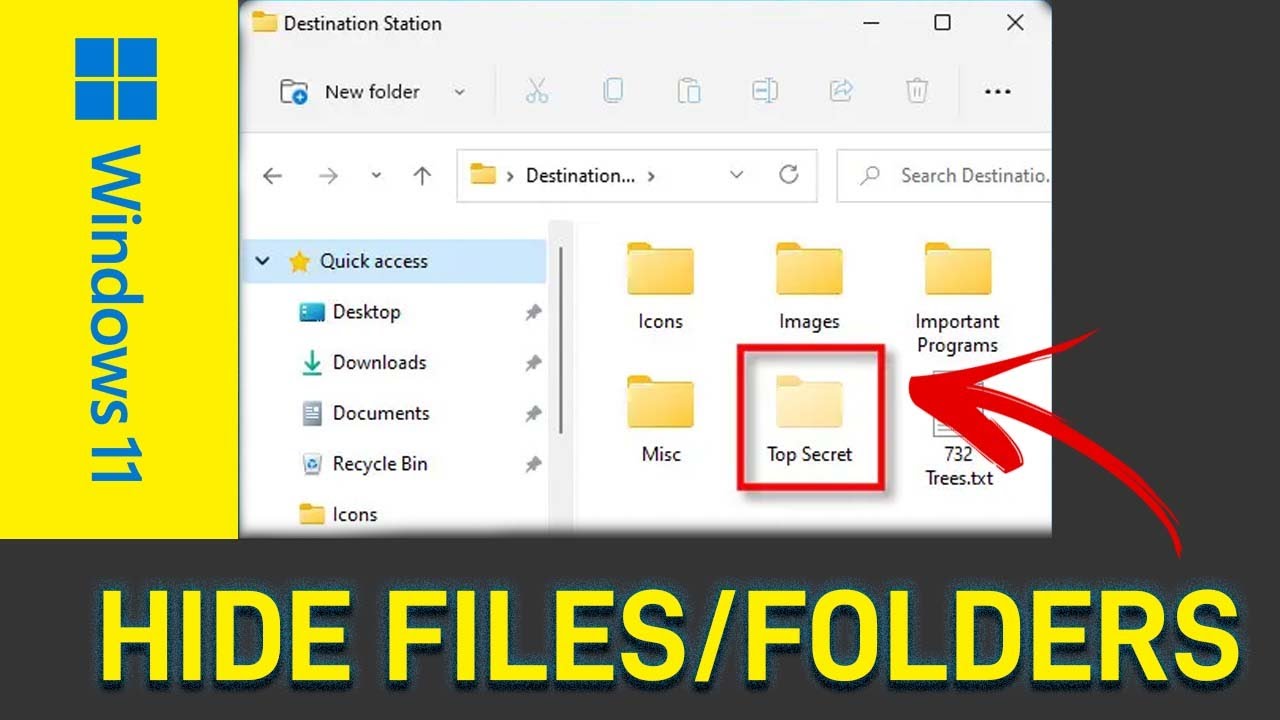
Sometimes, you have files or folders on your Windows PC that you’d rather keep out of sight. Maybe it’s sensitive personal data you don’t want casually stumbled upon, or perhaps it’s configuration files that shouldn’t be accidentally modified. Whatever the reason, Windows Explorer (now simply called File Explorer) offers a built-in feature to hide or unhide files and folders.
The concept of “hidden files” has been a part of operating systems for decades, tracing back to early command-line interfaces where files could be marked with attributes to control their visibility. This wasn’t primarily for security, but more for preventing accidental alteration of system files and decluttering directories. In modern Windows, while not a robust security measure, it serves a similar purpose: to keep less frequently accessed or critical system files out of everyday view, reducing clutter and the chance of unintentional deletion or modification.
This guide will walk you through the simple, step-by-step process of how to hide and unhide files and folders in Windows Explorer, ensuring you maintain control over your digital workspace.
Why Hide Files and Folders?
While hiding files is not a strong security measure (as they can be easily unhidden), it serves several practical purposes:
- Decluttering: Keep system files, application configuration files, or temporary folders out of your primary view, making your directories cleaner and easier to navigate.
- Preventing Accidental Deletion/Modification: By hiding crucial system files or personal backups, you reduce the risk of unintentionally deleting or altering them.
- Basic Privacy: For casual users, it can help keep sensitive personal documents or photos out of immediate sight from prying eyes, acting as a basic deterrent. However, it’s crucial to understand this is not a security feature against determined users or malware.
How to Hide Files and Folders in Windows Explorer
The process of hiding a file or folder is straightforward and involves changing an attribute of that item.
Method 1: Using File Explorer’s Properties Window
This is the most common and direct way to hide files or hide folders.
- Step 1: Open File Explorer.
- Click the File Explorer icon on your Taskbar (the folder icon) or press Windows key + E.
- Step 2: Navigate to the File or Folder.
- Browse to the location of the file or folder you wish to hide.
- Step 3: Access Properties.
- Right-click on the specific file or folder.
- From the context menu, select “Properties.”
- Step 4: Set the “Hidden” Attribute.
- In the Properties window, typically under the “General” tab, you will see a section labeled “Attributes.”
- Check the box next to “Hidden.”
- Step 5: Apply Changes.
- Click “Apply,” then “OK.”
- If you’re hiding a folder, a dialog box will appear asking if you want to apply changes to “This folder only” or “This folder, subfolders, and files.” Choose the appropriate option based on your needs. For most cases, selecting “This folder, subfolders, and files” is what you want for a hidden folder.
Once you click “OK,” the file or folder will disappear from view, provided your File Explorer settings are configured to not show hidden items.
How to Unhide Files and Folders in Windows Explorer
Once a file or folder is hidden, you need to adjust File Explorer settings to make it visible again. There are a couple of ways to do this, depending on your Windows version and preference.
Method 1: Using the “View” Tab in File Explorer (Windows 10/11)
This is the quickest and most modern way to unhide files or unhide folders.
- Step 1: Open File Explorer.
- Click the File Explorer icon on your Taskbar or press Windows key + E.
- Step 2: Go to the “View” Tab.
- In the File Explorer ribbon at the top, click on the “View” tab.
- Step 3: Check “Hidden items.”
- In the “Show/hide” group, you’ll see a checkbox labeled “Hidden items.”
- Check this box.
- Step 4: Locate the Hidden Item.
- Your hidden files and folders will now become visible. They will often appear slightly faded or translucent to indicate they are hidden items.
- Step 5: Unset the “Hidden” Attribute (Optional but Recommended).
- To permanently unhide an item (so it remains visible even if “Hidden items” is unchecked), you need to remove its “Hidden” attribute.
- Right-click on the hidden file or folder.
- Select “Properties.”
- Under the “General” tab, uncheck the box next to “Hidden.”
- Click “Apply,” then “OK.”
Method 2: Using Folder Options (Older Method, Still Works)
This method provides more granular control over visibility settings, including system files.
- Step 1: Open Folder Options.
- Open File Explorer.
- Click the “View” tab in the ribbon.
- Click “Options” on the far right, then select “Change folder and search options.”
- Alternatively, search for “Folder Options” (or “File Explorer Options”) in the Windows search bar and open it.
- Step 2: Navigate to the “View” Tab.
- In the Folder Options window, click on the “View” tab.
- Step 3: Adjust Hidden Files and Folders Setting.
- Under the “Advanced settings” list, scroll down to the “Hidden files and folders” section.
- Select “Show hidden files, folders, and drives.”
- While you’re here, you’ll also see an option: “Hide protected operating system files (Recommended).” This option is for highly critical system files. It’s generally recommended to leave this checked unless you have a very specific reason to uncheck it and know what you’re doing, as accidentally modifying these files can destabilize your system. If you do uncheck it, you’ll get a warning.
- Step 4: Apply Changes.
- Click “Apply,” then “OK.”
- Your hidden files and folders will now be visible, appearing slightly faded. To permanently unhide them, follow Step 5 from Method 1 above.
I’ve found myself using the “View” tab checkbox for “Hidden items” almost exclusively for quick toggling. The Folder Options method is more for when I need to dig into specific system file visibility settings.
Important Considerations When Hiding Files
- Not a Security Feature: As mentioned, hiding files is not a security measure. Any user with basic knowledge can easily unhide files using the methods described above. For true security, consider:
- Encryption: Using built-in tools like BitLocker (for drives) or third-party encryption software for individual files/folders.
- BitLocker: A full disk encryption feature included with some editions of Microsoft Windows that encrypts entire volumes.
- Password Protection: Using password-protected archives (like ZIP files with encryption) or applications that offer password protection.
- Access Permissions (NTFS Permissions): Setting granular NTFS permissions to restrict access to specific users. This is more advanced and typically used in multi-user or network environments.
- NTFS Permissions: A security feature of the NTFS (New Technology File System) file system that allows administrators to control who can access files and folders, and what actions they can perform (e.g., read, write, execute).
- Encryption: Using built-in tools like BitLocker (for drives) or third-party encryption software for individual files/folders.
- System Files are Hidden by Default: Many critical operating system files and program files are hidden by default to prevent accidental modification or deletion. It’s generally a bad idea to unhide and mess with these unless you know exactly what you’re doing.
- Search Functionality: Hidden files are still indexed by Windows Search and can be found if you search for them, even if they’re not visually displayed in File Explorer.
By understanding how to hide and unhide files and folders in Windows Explorer, you can better manage your digital space, reduce clutter, and provide a basic layer of visual privacy for your data.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the purpose of hiding files in Windows?
The primary purpose of hiding files in Windows Explorer is to declutter your view by keeping less frequently accessed or system-critical files out of sight. It also helps prevent accidental deletion or modification of important files by making them less visible during everyday use. It is not a robust security measure.
Q2: Is hiding a file the same as encrypting or password-protecting it?
No, hiding a file is not the same as encrypting or password-protecting it. Hiding simply makes the file invisible in File Explorer unless specific settings are changed. Anyone who knows how to enable “Show hidden items” can access it. Encryption and password protection use algorithms or passwords to truly secure the file’s content, making it unreadable without the correct key or password.
Q3: How do I make hidden files visible again in Windows Explorer?
To make hidden files visible again in Windows Explorer, simply open File Explorer, go to the “View” tab in the ribbon, and check the box next to “Hidden items” in the “Show/hide” group. The hidden files and folders will then appear, often with a slightly faded icon.
Q4: Can hidden files still be found by Windows Search?
Yes, hidden files are typically still indexed by Windows Search and can be found if you search for their names or content, even if they are not visually displayed in File Explorer. The hiding attribute only affects their visibility in Browse, not their existence or searchability.
Q5: Why are some folders like “AppData” hidden by default?
Folders like “AppData” are hidden by default because they contain crucial application data, settings, and temporary files that users generally don’t need to interact with directly. Hiding them prevents accidental modification or deletion, which could lead to application malfunctions or system instability.
Q6: Can I hide files on a USB drive or network drive?
Yes, you can hide files on a USB drive or a network drive using the same “Properties” method. However, the visibility of these hidden files will depend on the File Explorer settings of the computer you are accessing them from. If that computer’s File Explorer is set to show hidden items, they will be visible.
Q7: Is there a command-line method to hide/unhide files?
Yes, you can use the attrib command in Command Prompt to hide or unhide files.
- To hide a file: attrib +h “C:\Path\To\Your\File.txt”
- To unhide a file: attrib -h “C:\Path\To\Your\File.txt”
- To hide a folder: attrib +h +s “C:\Path\To\Your\Folder” (+s makes it a system file, further hiding it)
- To unhide a folder: attrib -h -s “C:\Path\To\Your\Folder”